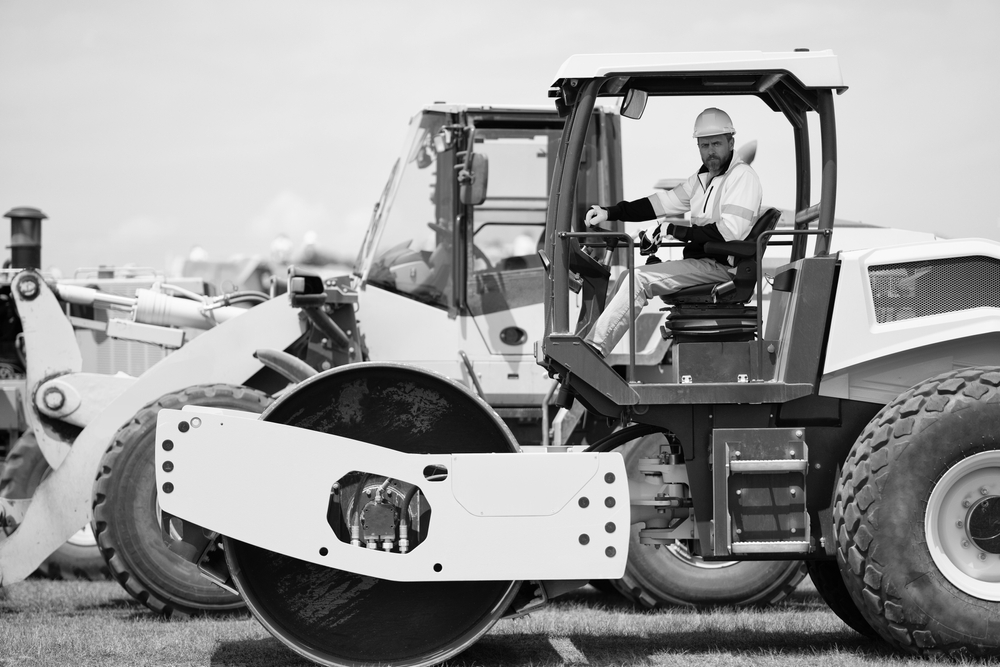
Understanding Off-Road Diesel
Off-road diesel, marked by its distinctive red dye, is crucial for the operation of vehicles and equipment not used on public roads. Its primary use in sectors such as agriculture, construction, and industrial manufacturing underscores its importance in non-urban environments where traditional services are limited. This type of diesel is specifically formulated to power heavy machinery and vehicles that are essential for development and production in remote areas.
Understanding the roles, regulatory environment, and economic implications of off-road diesel is paramount for businesses and consumers involved in these sectors to ensure they are maximizing efficiency while adhering to legal standards. Recognizing the breadth of its applications and implications not only aids in compliance but also optimizes operational costs and impacts environmental sustainability.
Common Uses of Off-Road Diesel
Off-road diesel powers a broad spectrum of machinery and vehicles critical to several key industries. Beyond its use in industrial settings and construction sites, it fuels a wide range of agricultural equipment, from harvesters to irrigation systems, which are vital for food production and resource management. It also supports the operation of generators and backup power systems across various sectors, providing reliability during power outages or in areas lacking infrastructure. In the maritime sector, off-road diesel is crucial for vessels involved in commercial and industrial activities, ensuring that operations such as towing, shipping, and fishing can proceed uninterrupted.
Additionally, off-road diesel is widely used in the mining industry, where its ability to power heavy-duty machinery like excavators and dump trucks is indispensable. Given its affordability compared to on-road diesel, many businesses in these sectors rely on it for cost-effective operations.
On-Road vs. Off-Road Diesel: A Detailed Comparison
While both on-road and off-road diesel serve as essential fuel sources, key differences distinguish them:
- Taxation: Off-road diesel benefits from tax exemptions since it is not meant for public roads.
- Dye and Regulation: Off-road diesel is dyed red to prevent illegal use on highways and is subject to different regulatory oversight.
- Sulfur Content: Off-road diesel historically had higher sulfur content, though modern regulations are pushing for ultra-low sulfur variants to align with environmental standards.
- Usage Restrictions: Off-road diesel is legally restricted to non-road applications, and improper use can result in severe penalties.
Taxation and Legal Implications
Understanding the taxation and legal aspects of off-road diesel is crucial for businesses. Governments provide tax exemptions for off-road diesel to support industries such as agriculture and construction, but these come with strict documentation requirements. Misuse, such as using off-road diesel in on-road vehicles, can lead to hefty fines and legal action.
To remain compliant, businesses must maintain accurate fuel usage records and adhere to regulations specific to their state or country. Keeping up with evolving tax policies and fuel rebate programs can also provide cost-saving opportunities.
Storage and Shelf Life Insights
Proper storage of off-road diesel is essential to maintain its quality and efficiency. The fuel should be kept in clean, dry tanks away from contaminants and moisture. Key considerations include:
- Storage Duration: Diesel fuel can degrade over time; using stabilizers can prolong its usability.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Cold weather can lead to gelling, requiring anti-gel additives.
- Tank Maintenance: Regular inspections help prevent contamination and bacterial growth.
Safety Protocols and Handling Practices
Safety is paramount when handling off-road diesel. To minimize risks, businesses should:
- Store diesel in approved, leak-proof containers.
- Train employees on proper handling techniques.
- Implement spill containment and cleanup measures.
- Adhere to fire safety protocols to prevent hazards.
Environmental Impact
The environmental concerns associated with off-road diesel are more pronounced due to its higher sulfur content compared to on-road diesel. This characteristic leads to significant emissions that can degrade air quality and contribute to the urban heat island effect. Additionally, off-road diesel’s substantial contribution to greenhouse gas emissions presents a challenge for achieving broader environmental goals, such as reducing global warming potential. Its impact on local ecosystems can be profound, particularly if spills occur, which can contaminate soil and water sources, affecting flora and fauna.
The management and reduction of these environmental impacts are critical, requiring strict adherence to best practices in fuel handling and proactive measures to seek cleaner alternatives that can provide similar levels of efficacy without the environmental cost.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory environment for off-road diesel is complex, governed by national and state agencies that impose standards to protect air quality and public health. These regulations, such as those enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and California Air Resources Board (CARB), are designed to gradually reduce the permissible levels of harmful emissions from diesel fuels. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for businesses to avoid significant fines and legal challenges.
Consumers must stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape, which includes monitoring updates to standards and adapting to new requirements. The penalties for non-compliance can be severe, involving not only fines but also reputational damage and potential operational shutdowns, underscoring the importance of regulatory awareness and proactive compliance.
Economic Considerations
Off-road diesel’s cost-effectiveness stems from tax exemptions and lower pricing compared to on-road diesel. However, businesses must account for factors such as:
- Fluctuating Fuel Prices: Global oil market trends can impact diesel costs.
- Operational Budgets: Fuel expenses constitute a significant portion of costs in industries reliant on diesel-powered machinery.
- Future Tax Changes: Governments may revise tax policies, affecting overall savings.
Strategic fuel procurement, efficiency optimization, and leveraging incentives can help businesses manage costs effectively.
Safety and Handling
Safety and handling of off-road diesel require strict adherence to established protocols to ensure both human safety and environmental protection. Proper storage practices are essential to prevent fuel degradation and minimize the risk of leaks and spills, which can lead to significant health and environmental hazards. The volatility of diesel necessitates robust safety measures to prevent fires and explosions, especially in environments with high operational risks like farms and construction sites.
Additionally, transportation of off-road diesel must comply with local and national regulations to ensure that it is carried out safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of accidents and ensuring the reliability of supply chains.
Maintenance and Performance
Equipment running on off-road diesel requires routine maintenance to ensure longevity and efficiency. Best practices include:
- Regular engine inspections and oil changes.
- Using fuel additives to prevent clogging and enhance performance.
- Adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
Proper maintenance not only enhances fuel efficiency but also reduces operational downtime and repair coxsts.
Tips for Consumers
Consumers using off-road diesel should:
- Verify that the fuel is marked with red dye.
- Understand specific fuel requirements for their machinery.
- Maintain compliance with legal and environmental regulations.
- Explore cleaner alternatives where possible.
Future Trends and Developments
The off-road diesel industry is evolving with advancements in cleaner fuels and sustainable energy solutions. Innovations such as biofuels and synthetic diesels are gaining traction, offering reduced emissions while maintaining efficiency. Additionally, stricter emissions regulations are expected to shape the industry’s future, encouraging businesses to adopt greener alternatives.
As the industry progresses, staying informed about these developments can help businesses make strategic decisions that align with sustainability goals.
The Importance of Informed Decision-Making
The use of off-road diesel plays a critical role in powering essential industries, but it also poses unique challenges and responsibilities for consumers. Understanding the full scope of off-road diesel’s applications, regulatory landscape, economic implications, and environmental impacts is crucial for making informed decisions.
As the industry continues to evolve, Fuel Me remains a dedicated partner, providing expert insights and innovative solutions that help consumers navigate these complexities. By staying informed and adaptable, consumers can ensure they are making choices that enhance their operational efficiency, comply with regulations, and contribute to environmental sustainability.